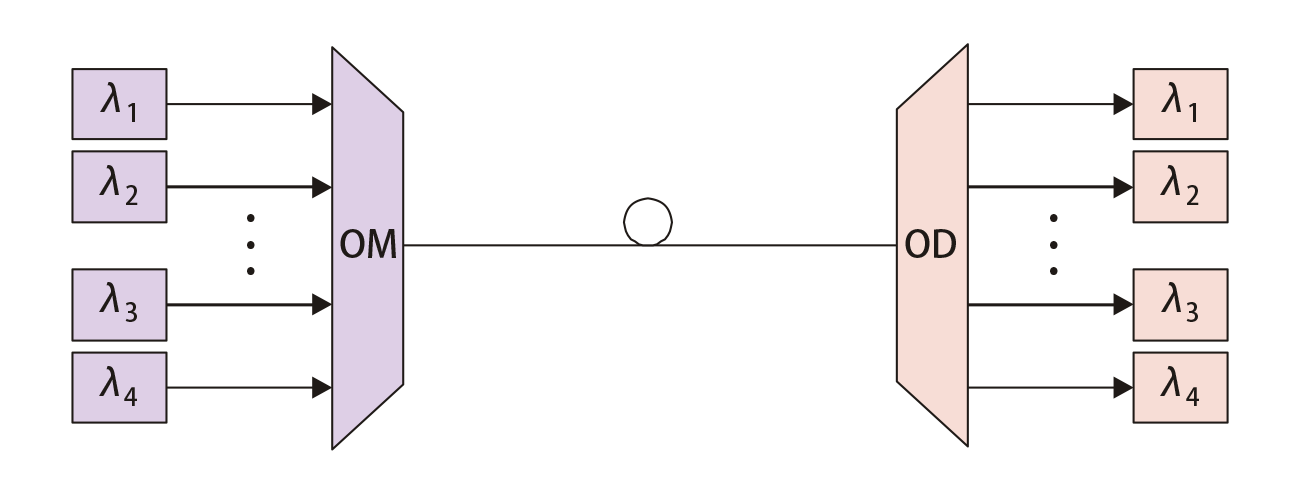
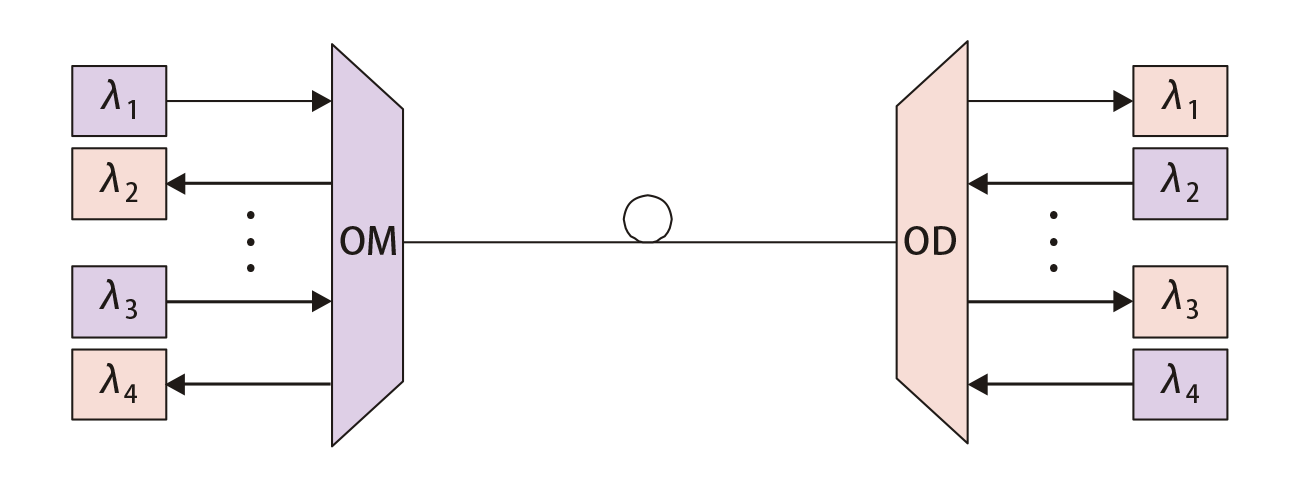
Unidirectional, as the name implies, only allowing transmission in one direction, while bidirectional allow transmission in two opposite directions. The following two figures show the typical optical transmission of unidirectional and bidirectional WDM systems.
Here the WDM network elements include an optical multiplexer (OM) and an optical demultiplexer (OD) (which are used as a pair with the opposing element).
Unidirectional WDM Systems
Unidirectional WDM is the transmission of all optical channels on a fiber propagating simultaneously in the same direction.
Bidirectional transmission is accomplished by use of either a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technique on a single fibre, or unidirectional transmission over two fibres.
Bidirectional WDM can lead (when a high number of channels is not required) to a reduction in the number of fibers and line amplifiers required, as compared to systems using unidirectional WDM.
In bidirectional WDM designs, several key systems issues should be taken into account. Care must be taken to avoid optical reflections in order to prevent multi-path interference. Some additional considerations are types and values of crosstalk, values and interdependence of power levels for both directions of transmission, OSC (Optical Supervisory Channel) transmission (if present), and automatic power shutdown or reduction.
Lfiber is a one-stop supplier of unidirectional and bidirectional WDM systems equipments. We offer unidirectional transmission over one single fiber, bidirectional transmission over one single fiber, bidirectional transmssion over two fibers and ring network etc.
Click the following link to learn more and Discover the Fiber-optic World.