Capacity of WDM Fiber Optic Communication Systems
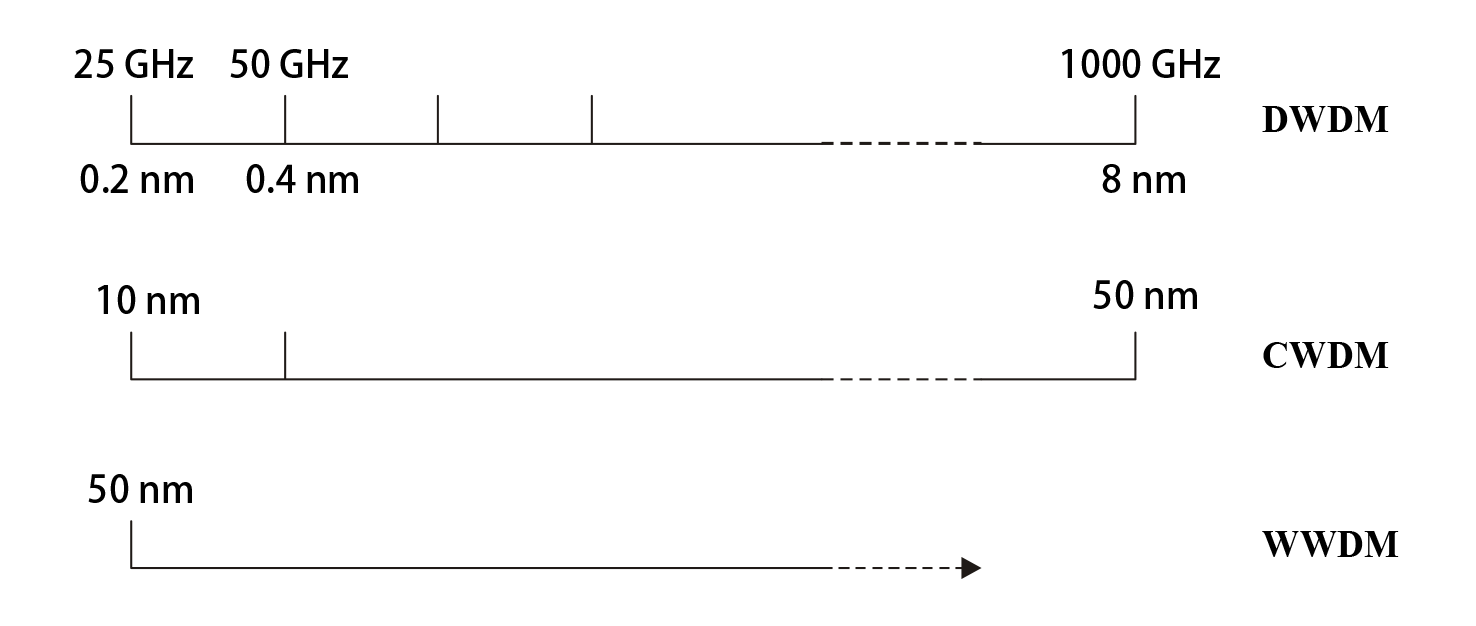
The ultimate capacity of a WDM fiber system depends on how closely optical channels can be packed in the wavelength domain. In the case of dense WDM (DWDM) applications optical channels are very densely spaced. For this case of DWDM applications the so-called “channel spacing” is expressed in the frequency domain. The maximum number of channels in a DWDM system operating in a given spectrum band (e.g. 1530-1565 nm for the C-band) is determined by the channel spacing.
Definition of Channel Spacing
Channel Spacing in DWDM, CWDM and WWDM Fiber Optic Systems
There are three categories of WDM systems:
Coarse WDM (CWDM)
CWDM have a channel wavelength spacing less than 50 nm, but greater than 1000 GHz (about 8 nm at 1550 nm and 5.7 nm at 1310 nm). The value of “c” (speed of light in vacuum) that should be used for converting between frequency and wavelength is 2.99792458 × 108 m/s; Devices within this class can cover several spectral bands.
Dense WDM (DWDM)
Wide WDM (WWDM)
Click the following link to learn more and Discover the Fiber-optic World.
